by Joseph Williams
It’s been one thing after another with the new-but-not-necessarily-improved Free Application for Federal Student Aid, a form that helps students pay for college.
First, the long-anticipated rollout of the redesigned online application was delayed for three months because it just wasn’t ready. Then, when it finally did appear, a variety of bugs and glitches, including some that could reduce the amount of federal tuition aid, kept students and their families from completing it. Now, Chronicle of Higher Education reports that schools are receiving FAFSA applications with incorrect tax information from families.
None of this is good news for Black students, some 80% of whom depend on FAFSA to help pay for ballooning college costs.
According to the nonprofit National College Attainment Network, roughly 34% of all eligible high school seniors have submitted FAFSA applications through March 22, an overall decline of nearly 29% since last year. But the problem is most acute, according to NCAN data, among low-income schools and schools with high concentrations of minority students. There, the percentage decline in 2024 FAFSA applications is slightly more than 35%.
Besides worsening an already-bad time crunch for colleges and students who needed the financial information weeks ago, the FAFSA fiasco could keep Black students — an outsized number of whom rely on federal aid — out of college classrooms this fall.
“Because Black students are disproportionately FAFSA filers, this has a huge impact on their ability to make a decision about both where, and if, they go to college,” says Bryan Cook, director of higher education policy at the Urban Institute Center on Education Data and Policy.
Cook worries that some frustrated Black students, worried that they can’t pay for college without federal assistance, may downgrade their college choice or give up on college completely. Either option, he says, would have negative, long-term effects on their earning power in the job marketplace.
The FAFSA process, which colleges use to calculate their share of financial aid for a student, is already months behind schedule, Cook says. Unless the problems get resolved quickly, he says, ”Black students are going to have to make some really tough decisions about whether or not they continue to stay in this process.”
The unequal impact on Black college-bound seniors is the latest headache for the federal Ed Department’s FAFSA reboot, which stumbled out of the gate late last year.
Instead of the FAFSA application being open Oct. 1, enough time for students and colleges to prepare for the fall 2024 semester, the form didn’t launch until Dec. 31, setting off a scramble. The subsequent series of errors and submission problems didn’t help; at last count, only around 20% of applications have been processed, resulting in a nationwide backlog of some 6 million applications.
Even though the Ed Department delayed the rollout to fix problems it knew about, a technicality it overlooked could end up costing students almost $2 billion in aid. And that’s before the cascade of issues that have surfaced in recent months.
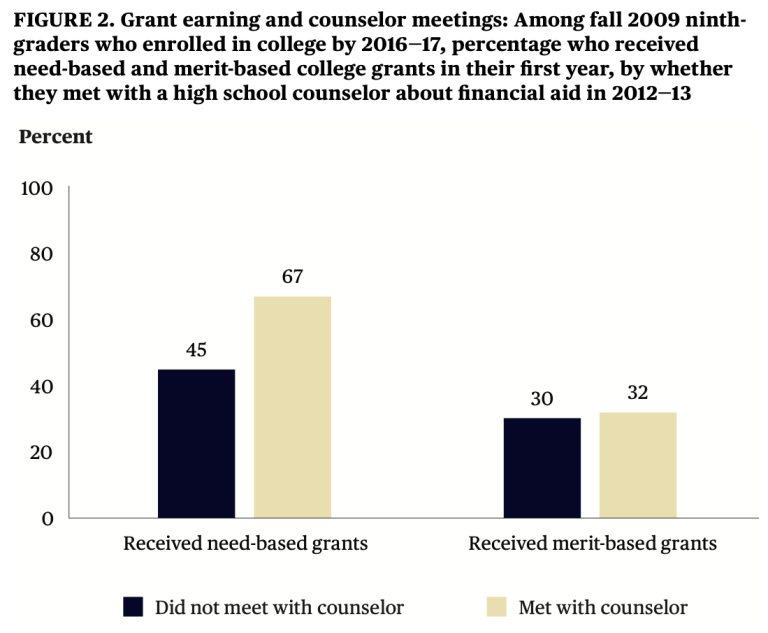
Cook says those numbers are exacerbated by the fact that low-income, high-minority schools have fewer guidance counselors who can help guide students through the process. That can be important, experts say, because heads of low-income minority households tend to have lower rates of college degree attainment.
“We know that Black and Hispanic students disproportionately attend high-poverty schools, where their ratio of guidance counselors to students is double what that what they are in more wealthy schools,” he says. “So the combination of Black students disproportionately filing FAFSAs and disproportionately having less access to guidance counselor’s means that this issue with the rollout of the new FAFSA is having a much harder impact on black students.”
Indeed, studies have found that Black students are 1.2 times more likely than white students to attend a school with a law-enforcement officer but without a guidance counselor. The counselors can be critical to completing the FAFSA.
And every bit of financing helps: According to a study by College Board, for the 2022-23 academic year, average tuition and fees for a public four-year school averaged $10,940 for in-state students and $28,240 for out-of-state students, according to the latest data from College Board. Private nonprofit four-year schools amassed a much higher $39,400 average. Add room and board, books, and other expenses to the mix, and that bill goes up several thousand dollars more.
Given those hurdles, Cook worries that Black student enrollment in college — already on the decline in part because of skyrocketing tuition and the Supreme Court dismantling of affirmative action in school admission decisions — is about to take another hit because of the FAFSA snafu.
Students depend on the financial aid form to get “a better sense of what schools they can afford,” he says. That matters, he says, because a degree from a more selective college tends to bring higher wages after graduation.
Without knowing how much federal aid they’ll get for tuition, “high school students may decide to now go to maybe a regional, public school that’s more affordable, or even a community college that they can afford,” Cook says. “Or — worst case scenario — opting out of pursuing a college education this year, altogether. And we know any sorts of delay for low income students could ultimately mean they choose not to go on to college.”
Fortunately, Cook says, many colleges are doing what they can to help, pushing back deadlines and trying to work with students. But the ripple effects of the FAFSA revamp, Cook says, spotlights the bigger, thornier problem of college affordability.
“I think it just underscores how much of a reliance students have on federal financial aid,” he says. Unfortunately, “there is no silver bullet.”
“My biggest fear,” Cook says, “is that we may have already lost some students.”